Silent Cyber: The Missing Piece in Your Business's Cybersecurity Puzzle

Technology is the backbone of most businesses, but the risk of cyber attacks comes with that reliance. As these threats keep changing and getting sneakier, companies must protect their operations and assets by being vigilant about cybersecurity. One often overlooked aspect is “silent cyber” and the importance of cyber insurance. This insurance can be a valuable safety net when the unexpected happens.
What is silent cyber?
Before diving deeper, let’s introduce the concept of silent cyber to those unfamiliar with the term. In the insurance industry, when a business insurance policy doesn’t explicitly state whether it covers or excludes certain risks, it’s called “silent.” Silent Cyber describes how traditional insurance policies, such as general liability, were not designed to cover costly cyber incidents. Historically, insurance policies might not have explicitly mentioned cyber threats, leaving policyholders in the dark about whether their coverage extends to cybersecurity incidents. This ambiguity has created a gray area where insurers and policyholders can find themselves entangled when determining coverage for cyber events. To complicate matters further, several insurance providers have added cyber exclusions on their property and liability forms to clarify their coverage intent.
How standard insurance can fall short against cyber attacks
Many businesses remain blissfully unaware of the gaps in their insurance policies, with only 26% having standalone cyber insurance policies. A company might assume its general liability policy provides adequate protection against a data breach, only to discover the hard way that it doesn’t.
Often, insurance policies offer minimal coverage for cyber claims, with low limits or only third-party liability coverage. They may lack provisions to protect the insured’s own losses, leaving businesses vulnerable to severe financial consequences. Cyber extortion losses, such as ransom demands, are frequently excluded, leaving victims to grapple with extortionists’ demands.
The consequences of inadequate cyber insurance coverage
Not having proper cyber liability insurance can have serious consequences. The expenses associated with a cyber attack can add up quickly, including the cost of containing the breach, hiring computer forensic experts, legal defense costs and loss of business income if systems need to be shut down. In some cases, businesses have even gone bankrupt due to the financial strain caused by a cyber incident.
Consider this: The cost of a data breach rose 15% to $4.45 million globally in 2023.
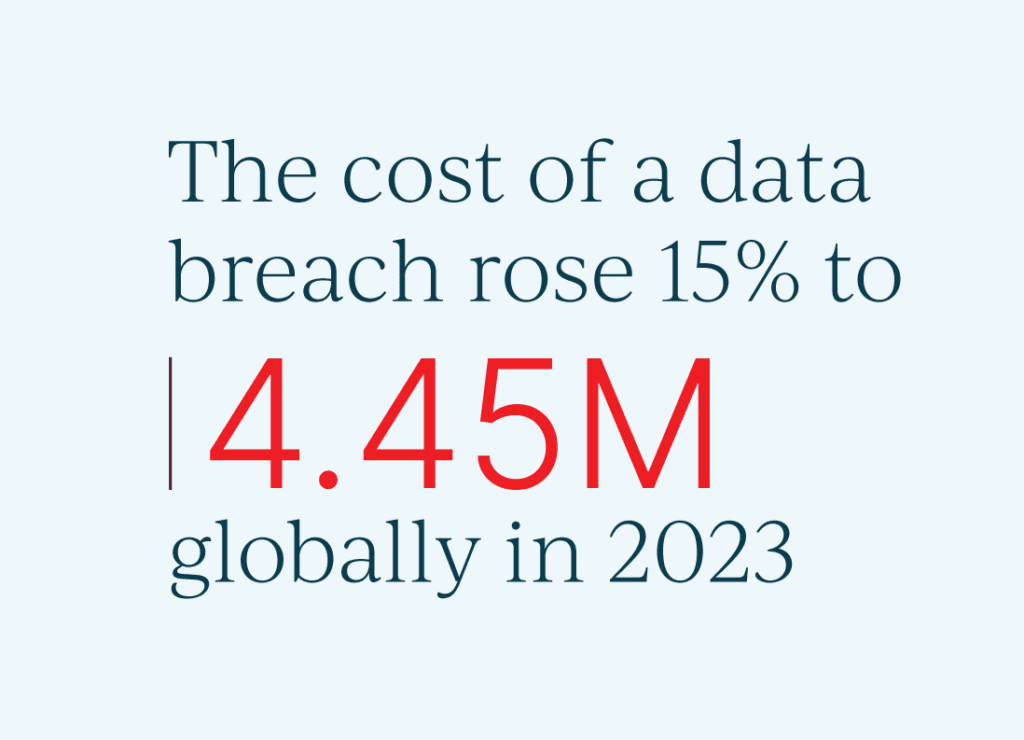
This alarming trend highlights the growing financial threat posed by cyber attacks. And the consequences of these data breaches are not confined to the digital realm. They reverberate throughout the real world, causing tangible harm to businesses, individuals and society.
Let’s take the Equifax data breach of 2017 as an example. The attack led to the compromise of the personal data of 147 million Americans. As a result, Equifax had to pay a settlement of $700 million, which highlights the high cost of a data security breach caused by inadequate cybersecurity measures.
The 2021 Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack is another stark reminder of the physical implications of cyber threats. This incident disrupted fuel supplies across the Eastern United States and demonstrated how vulnerable critical infrastructure can be to cyber attacks.
The rise in data breaches indicates a broader trend—the growing sophistication of cyber threats. Hackers and cybercriminals have evolved from lone actors operating out of their basements to well-funded, organized criminal enterprises. They exploit vulnerabilities in software, employ advanced malware and leverage social engineering techniques to breach even the most robust defenses. These attacks are not limited to government entities; they target private enterprises, intellectual property and critical infrastructure.
Types of cyber liability insurance coverage
With data breaches, ransomware attacks and other cyber threats on the rise, it has become imperative for organizations to protect themselves against the potentially devastating financial losses and reputational consequences of such incidents.
Cyber liability insurance, also known as cyber insurance or cyber risk insurance, is designed to provide financial protection and support in the event of a cyber attack or data breach. It has evolved rapidly in response to the ever-changing cyber threat landscape, offering various types of coverage to address the diverse risks businesses face. Let’s dive into the different types of coverage you can find in a typical cyber liability insurance policy.
First-party coverage:
- Data breach response: This covers the costs of responding to a data breach, including notifying affected individuals, providing credit monitoring services and managing public relations.
- Business interruption: In the event of a cyber attack that disrupts your operations, this coverage can compensate for lost income and additional expenses incurred during the downtime.
- Cyber extortion and ransomware: This covers the costs of negotiating with cybercriminals who have hijacked your data and demand a ransom, as well as the ransom payment itself (if it’s a covered expense).
Third-party coverage:
- Network security and privacy liability: Protects your business from liability claims and legal costs resulting from a data breach or cyber attack, including claims from affected customers or partners.
- Regulatory and legal defense: This covers the legal costs of defending against regulatory investigations and lawsuits related to a data breach or cyber incident.
- Media liability: Protects against claims of defamation, copyright infringement or other intellectual property issues arising from online content.
Cybercrime events coverage:
- Computer and funds transfer fraud: Cybercriminals are becoming increasingly sophisticated, often tricking businesses into transferring funds to fraudulent accounts. This coverage helps recover the stolen funds or covers the financial loss resulting from such fraudulent activities.
- Social engineering fraud: This form of cybercrime involves tricking employees into harmful actions, like divulging sensitive information or transferring money, and cyber liability insurance can help protect your business against such losses.
Assessing your needs and risk profile for tailored coverage
A cookie-cutter insurance policy may leave you vulnerable to unforeseen challenges. No two businesses are alike, and neither are their cyber risk exposures. It’s crucial for companies to carefully assess their specific needs and risk profile to select the most suitable insurance coverage. This comprehensive process involves several key steps:
➤ Safeguarding sensitive data
Identifying sensitive information, including client data, financial records and proprietary algorithms, is at the heart of any cybersecurity assessment. Once identified, it’s imperative to determine the locations within your systems where this critical data resides. This meticulous mapping helps understand potential weak points and forms the foundation for effective risk mitigation.
➤ Implementing robust safeguards
The next step is implementing measures to safeguard this data with a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy, including firewalls, encryption, access controls and employee training. The goal is to create multiple layers of defense to deter cyber threats and minimize the potential damage in case of an incident.
➤ Backing up data
Data is the lifeblood of modern businesses, and its loss can be catastrophic. A critical aspect of risk mitigation is data backup. Regular, automated backups ensure that your organization can recover essential information swiftly and minimize downtime even in the worst-case scenario.
➤ Formulating a comprehensive incident response plan
An incident is not “if” but “when.” Having a well-thought-out response plan is paramount. This plan should include clear procedures for detecting, reporting and mitigating cyber incidents. Additionally, it should outline the steps to take in the aftermath of an attack, including communication strategies, legal considerations and public relations efforts. An incident response plan is your roadmap to navigating the often chaotic aftermath of a serious cyber event or breach.
➤ Testing and refining your plan
Creating an incident response plan is one thing, but ensuring its effectiveness is another. Rigorous testing and simulations are crucial in identifying and refining weaknesses in your program. A well-tested plan can make all the difference in minimizing the impact of a cyber incident.
➤ Transferring risk through insurance
Assessing your organization’s cybersecurity needs is ongoing, not a one-time task. It is crucial to evaluate your business needs and risk profile to determine the level of risk your organization can comfortably retain. Typically, this amounts to around 90-95% of the risk, and the remaining portion should be transferred to a cybersecurity insurance policy. This policy serves as a safety net, providing financial protection and resources in the event of a significant cyber incident.
Remember that a proactive approach is the best defense for cybersecurity.
Industry-specific regulations and impact on insurance
Healthcare and finance are industries exposed to unique cyber security threats that require them to grapple with complex regulatory frameworks that govern their operations. These industries not only have to fend off threats but also adhere to strict regulatory requirements. For example, healthcare organizations in the United States must abide by the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), while financial institutions need to comply with the Payment Card Information Data Security Standard (PCI-DSS). These regulations demand meticulous data protection and privacy safeguards, making their cybersecurity strategies more complex.
Privacy regulations also play a critical role in shaping the cyber insurance landscape. Regardless of a company’s location or headquarters, it must stay well-informed about federal and state privacy laws. For instance, the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) are prime examples of global privacy regulations that transcend geographical boundaries. GDPR applies to any organization processing the personal data of EU citizens, extending beyond the EU, while CCPA enforces stringent privacy standards on businesses operating in California, irrespective of their primary location. These global and state-level regulations have far-reaching implications, and companies must invest in robust cybersecurity measures and secure comprehensive cyber insurance to mitigate the legal and financial consequences of potential data breaches.
The increasing legal and financial consequences of data breaches have made it more urgent for small businesses to strengthen their cyber defenses and invest in robust cyber insurance policies.

Strengthening cybersecurity protection beyond insurance
While cyber liability insurance is crucial, it’s only one piece of the cybersecurity puzzle. To strengthen defenses against cyber threats, businesses should implement best practices such as:
- Two-factor authentication (2FA): Enable 2FA for all applications and accounts to bolster login security.
- Access management: Separate privileged service accounts from regular users and tightly manage access controls.
- Endpoint protection: Safeguard all user endpoints (devices) to prevent breaches.
- Patch management: Install system patches promptly, especially critical updates.
- Anti-phishing campaigns: Conduct anti-phishing campaigns for employees and regularly test their ability to detect and thwart email compromises.
It’s best to combine strong cybersecurity practices rather than choose between them.
The road to cyber resilience: what every business needs to know
Cybersecurity is complex. One of the most effective ways to protect your small business is to seek guidance from trustworthy advisors.
Cyber IT security experts can help you identify vulnerabilities in your systems that might go unnoticed by in-house teams. They can conduct thorough assessments, employing the latest tools and techniques to pinpoint potential weak spots in your network, software and data storage solutions. This information allows you to develop robust strategies and action plans to minimize these cyber risks further.
Insurance carriers are also recognizing the growing need for cyber risk mitigation. Many now offer pre-breach services for free. These services can be invaluable for businesses looking to proactively address threats. Pre-breach services typically include proactive risk assessments, vulnerability scans and employee training. By utilizing these services, you can proactively detect and remedy vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them. This not only minimizes the risk of a cyberattack but also demonstrates your commitment to cybersecurity to customers and partners.
Don’t wait for a cyberattack to happen. Take proactive measures to secure your business and its future. If you’re unsure about the best cyber coverage for your business, contact Crane Agency.

